Understanding the Total Alkalinity (TA) and pH Relationship & How They Work Together
Total alkalinity (TA) and pH are two of the more essential aspects of water maintenance. In basic pool chemistry terms, pH determines water acidity and TA acts as a “buffer” to reduce wild pH swings.
Understanding the relationship between pH and TA is critical in water health and ensuring effective chemistry balance.
pH and Total Alkalinity Work Together
pH determines pool water’s acidity or basicity (“alkaline”). More broadly, pH measures the number of free hydrogen ions or hydroxyl ions in water. More free hydrogen ions are acidic, while more free hydroxyl ions are basic.
pH is measured on a logarithmic scale from 0 to 14. Each unit increase is 10 times the previous number (ex: 5 is 10 times more acidic than 6 and 1,000 more acidic than 8)

A pH of 7 is considered “neutral” which means anything below 7 is acidic water and above 7 is basic water.
Total alkalinity (TA) measures water’s ability to resist changes in pH. Scientifically speaking, it acts as a buffer, a chemical system that resists any change upon the addition of acids or bases.
If the water contains no buffer, then the pH can change or bounce dramatically.
Many events can cause pH to rise and fall daily. Rain, splashing, and using water features can increase pH.
Alkalinity is there to “neutralize” any change and help keep pH as stable as possible. It does not determine pH levels but rather holds them steady.
Unbalanced Total Alkalinity and pH Will Cause Water Issues
If TA is too low, pH bounce can occur. Conversely, a high TA will also make it more difficult to adjust pH on a normal basis
Water that has a low pH (acidic water) can do some serious damage to equipment, from dissolving metal surfaces like ladders to wrinkling pool liners.
Similarly, higher pH levels (basic water) can introduce scaling, reduce circulation and cause water cloudiness.
Alkalinity that is balanced will regulate how quickly pH can move.
Adjust pH or Total Alkalinity First?
In general, with the relationship between TA and pH, pH should be your main focus to balance. Keep pH between 7.2 and 8.0. Water that is a little more basic promotes better bather comfort.
TA should be somewhere between 50 to 90 ppm. Any measurement lower than 50 should be increased.
However, first, let TA find its own balance with pH levels. If pH remains stable with a higher TA, then that is OK. Only when pH seems to dramatically change on a daily basis should TA be the focus point.
This might be a newer concept to understand and will go against industry norms of acceptable TA limits. You may read to keep TA higher around 100 – 150 ppm.
The main reason for that recommendation is most pool owners use trichlor pucks as their chlorine of choice. Trichlor is highly acidic and will drive pH and TA down over time.
The higher TA levels are suggested to counteract that acid addition in the water. Liquid chlorine or cal hypo is more “pH neutral” and will have less of an effect on overall pH levels, so if these are what is used for daily chlorination, the lower TA levels are fine.
Pool Chemicals That Impact pH and Total Alkalinity
Muriatic acid or dry acid is the preferred method when lowering both pH and total alkalinity. When using muriatic acid, please use proper PPE: gloves, goggles, and a mask as the fumes can be dangerous to breathe.
Klean Strip Green Muriatic Acid used to lower pH and TA in swimming pools.
Keep in mind, acid will not lower both by the same amount, so be careful with the additions. As a general rule, if using acid at 31.45% strength, a 10 ppm decrease in TA will cause a .6 decrease in pH.
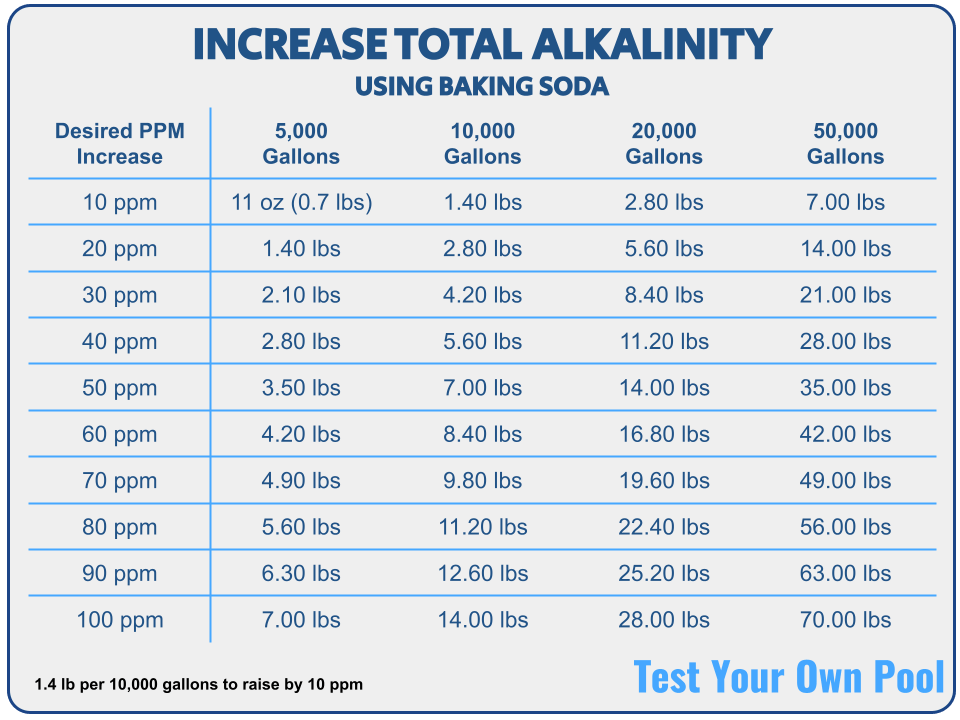
Alkalinity can be increased with baking soda. Now you know the secret to baking cakes while increasing TA!
In terms of baking soda quantity, add about 1.4 lbs per 10,000 gallons to raise TA by 10 ppm. Refer to the chart below or use our total alkalinity calculator.
pH rises naturally over time. It rarely has to be raised manually unless too much acid has been added to the water. The easiest way to raise it is to have a pool party as aeration will increase pH levels.
pH can also be increased with borax, a common laundry detergent cleaning agent. It can be found in most grocery stores in the detergent aisle under the name 20 Mule Team. Soda ash can also raise pH, but this will also raise TA slightly.
Always Remember, Testing Sustains the Relationship!
It is nearly impossible to know pH and TA levels without water testing, let alone understand the relationship and chemistry balance between the two.
Keep the pH in check, and TA will find its landing spot on its own!


